Using Blockchain to Brings Trust and Transparency to the Financial Sector
How can we create networks for data and financial transactions that increase and drive innovation while increasing security and advancing efficiency? IBM scientists are convinced they have the answer: blockchain technology.
IBM Research - Haifa brings its rich expertise in applied research in the area of blockchain to the INFINITECH consortium. Blockchain technology will be applied to such areas as data sharing, knowing your customer (KYC), and consent management in the scope of the project. IBM Research - Haifa is involved in all the blockchain-related activities in INFINITECH, and is specifically leading the blockchain implementation efforts.
Blockchain has proven to be a disruptive technology in the financial sector. In fact, among all industries, the financial sector has been working with blockchain the longest. In Forbes’ list of the 50 top blockchain companies in 2020, financial services was the leading solution area by a large margin (39%), focused mainly on cross-border payments, digital asset trading, and digital/cryptocurrency. According to the latest IDC European Tech and Industry Pulse Survey, there is a significant increase in current (from 5% to 16%) and planned adoption (from 5% to 18%) of blockchain and distributed ledger technologies (DLTs) among all industries and countries. Among financial markets, banking has the highest current and planned adoption of blockchain (53%). Banking is driving investments in this space, while insurance is just slightly below the average (33%). The IDC survey is a landmark study of IT solutions, investment priorities, and emerging technologies in over 77% of the European economy. The sample consists of 2,793 organizations across nine European vertical markets.
How can we create networks for data and financial transactions that increase and drive innovation while increasing security and advancing efficiency? IBM scientists are convinced they have the answer: blockchain technology.
Blockchain is a peer-to-peer network and a distributed ledger technology allowing any participant in the business network to see the ground truth system of record (ledger). Each participant has an exact up-to-date ledger that reflects the most recent transactions or changes. Figure 1 shows the conceptual differences in the networks before and after applying blockchain technology – in this case, Hyperledger Fabric.
In traditional networks, each participant keeps their own ledger(s), which are updated to represent business transactions as they occur. This is expensive due to duplication of effort and intermediaries adding margin for services. It is clearly inefficient, as the business conditions – the contract – is duplicated by every network participant. It is also vulnerable because if a central system (e.g., a bank) is compromised due to an incident, this affects the whole business network. Incidents can include fraud, cyber-attack, or even a simple mistake. The novel blockchain architecture gives participants the ability to share the ledger, which is updated every time a transaction occurs through peer-to-peer replication. Cryptography is used to ensure that network participants see only the parts of the ledger that are relevant to them, and that transactions are secure, authenticated, and verifiable. Blockchain also allows the contract for asset transfer to be embedded in the transaction database, determining the conditions under which the transaction can occur. The ledger serves as the single source of truth for all transactions in the network, thus providing a full history of the transactions (provenance), transparency, traceability, and a non-repudiation process.
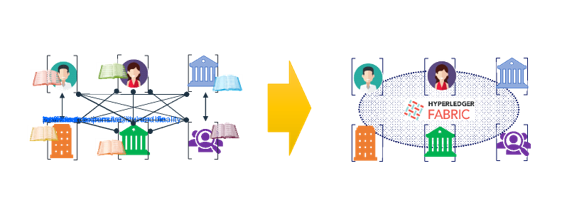
Figure 1: Financial networks before and after blockchain. Use of blockchain technology such as Hyperledger Fabric converts vulnerable and inefficient transactional networks to secure and transparent networks that provide a single source of truth for all transactions.
IBM Research - Haifa is applying the Hyperledger Fabric blockchain in the INFINITECH pilots. The technology is an open source, industrial-grade implementation of a private or permissioned blockchain most suitable for enterprises. IBM is the main contributor of the Hyperledger Fabric project under the Linux foundation. The solution is considered the most mature and popular blockchain platform and the platform of choice across all industries: 48% of covered projects that are used in production have chosen Hyperledger Fabric as the core protocol framework underlying the network. (1)
IBM Israel Science and Technology Limited, better known as IBM Research - Haifa, was first established in 1972. Since then, the lab has conducted decades of research vital to IBM’s success. The lab is the largest IBM research laboratory located outside the United States with close to 500 researchers, 25 percent of whom have doctorate degrees in computer science, electrical engineering, mathematics, and related fields. IBM has a strong track record in these areas, both academic and industrial, as well as within EU-funded projects.
(1) https://www.jbs.cam.ac.uk/fileadmin/user_upload/research/centres/alternative-finance/downloads/2019-ccaf-second-global-enterprise-blockchain-report.pdf